Diffuse water pollution in urban areas is a serious environmental problem worldwide. Urban diffuse pollution enters the urban water catchment through different processes such as runoff. Urban water runoff (UWR) can be highly polluted with suspended solids, nutrients, heavy metals, PAHs and microplastics among others.
The implementation of UWR treatment systems is key to avoid harm to ecosystems and human health. For this, WATERUN will implement and optimize Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) techniques as a decentralized, sustainable and efficient UWR treatment. Aarhus case study includes 4 SUDs (2 wet detention ponds and 2 infiltration systems) located in different types of catchments (Traditional Urban developments, Residential areas and Mixed urban areas/ light industry) within the municipality of Aarhus.
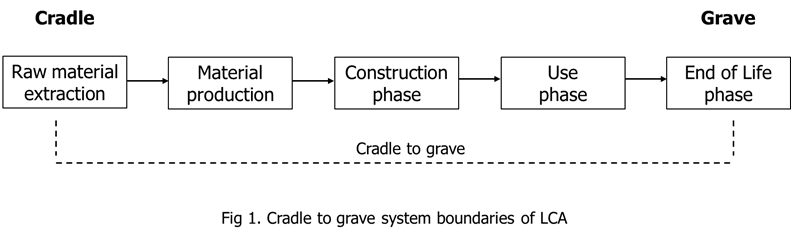
Since the implementation, operation and decommissioning of UWR treatment systems causes environmental damage, AIMEN will monitor and quantify the SUDS environmental footprint. For this, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology, an internationally standardised method, will be used following ISO14040 and the ILCD Handbook. Thus, LCA will comprise four phases: the goal and scope definition phase, the life cycle inventory (LCI) analysis phase, the life cycle impact assessment (LCIA) phase and the life cycle interpretation phase. AIMEN will use the software SimaPro v9.6 with the Ecoinvent 3.10 database for the LCA. The method to be used is the ReCiPe midpoint and endpoint method. The functional unit established for the LCA is 1 m³ of treated water. The scope of the LCA was defined from cradle to grave (Figure 1), thus taking into account all stages of the SUDs life cycle from the extraction of raw materials (cradle) to end-of-life (grave).
Authors: Valeria, Acevedo García, AIMEN, valeria.acevedo@aimen.es